如何在 Linux 中创建 Systemd 服务单元
Systemd 是一个现代软件套件,它在 Linux 系统上提供许多组件,包括系统和服务管理器。它与 SysV 和 LSB 初始化脚本兼容,可作为 sysvinit 的替代品。
systemd 服务在单元文件中定义(单元是服务和系统资源的表示,例如设备、套接字、挂载点等)。自定义服务单元文件应存储在 /etc/systemd/system/ 目录中,并且必须具有 .service 扩展名。例如,自定义 test-app 服务使用 /etc/systemd/system/test-app.service 单元文件。
单元文件是纯文本 ini 样式文件,通常包括三个公共部分。第一部分通常是 Unit 部分,其中包含与单元类型无关的有关单元的一般信息。
下一部分是单元类型部分,对于服务,它是一个服务部分。最后一部分是 Install 部分,其中包含设备的安装信息。
在本指南中,我们将展示如何在 Linux 中创建一个新的 systemd 服务并使用 systemctl 命令管理该服务。
在 Linux 中创建自定义 Systemd 服务文件
要在 systemd 下将应用程序或程序或脚本作为服务运行,您可以按如下方式创建新的 systemd 服务。首先创建名为 test-app.service 的服务 unit 文件(请记住将 test-app 替换为您的服务或应用程序的实际名称), 在 /etc/systemd/system/ 下:
# vi /etc/systemd/system/test-app.service
以下配置用于定义使用 Gunicorn(用于 UNIX 的 Python WSGI HTTP 服务器)运行 Flask 应用程序的服务。
[Unit]
Description=Gunicorn daemon for serving test-app
After=network.target
[Service]
User=root
Group=root
WorkingDirectory=/apps/test-app/
Environment="PATH=/apps/test-app/bin"
ExecStart=/apps/test-app/bin/gunicorn --workers 9 -t 0 --bind 127.0.0.1:5001 -m 007 wsgi:app --log-level debug --access-logfile /var/log/gunicorn/test_app_access.log --error-logfile /var/log/gunicorn/test_app_error.log
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
让我们简要描述一下上面配置中的每个配置指令:
- 描述 – 用于指定服务的描述。
- After – 定义与第二个单元 network.target 的关系。在这种情况下,test-app.service 在 network.target 单元之后被激活。
- 用户 – 用于指定将使用其权限运行服务的用户。
- Group – 用于指定将使用其权限运行服务的组。
- WorkingDirectory – 用于设置执行进程的工作目录。
- Environment – 用于为执行的进程设置环境变量。
- ExecStart – 用于定义在启动此服务时执行的带有参数的命令。
- ExecReload – 用于定义要执行的命令以触发服务中的配置重新加载。
- WantedBy – 允许在每个列出的单元的
.wants/或.requires/目录中创建符号链接( s), multi-user.target 在这种情况下,当使用 systemctl enable 命令 启用 test-app.service 单元时。< /li>
您可以找到所有服务单元配置参数,在服务单元配置文档中有详细描述。
保存单元文件并关闭它。然后通过运行以下命令用这个新的服务单元文件重新加载 systemd:
# systemctl daemon-reload command
请记住在编辑单元文件后始终运行此命令。
在 Linux 中管理 Systemd 服务
要启动/激活服务,请运行 systemctl 命令,如下所示:
# systemctl start test-app.service
要检查服务是否正在运行,请发出 systemctl 命令,如图所示。
# systemctl status test-app.service
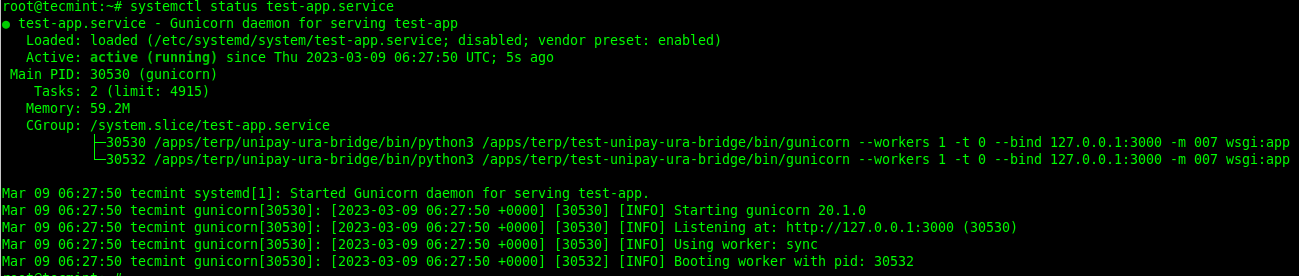
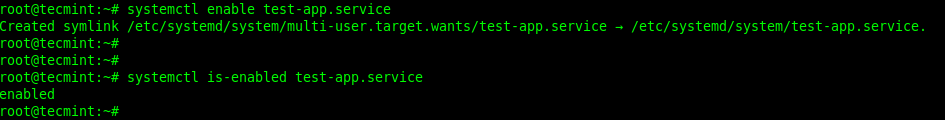
要使服务在系统启动时启动,请使用 systemctl enable 命令。您可以使用 systemctl is-enable 命令检查服务是否已启用,如下所示:
# systemctl enable test-app.service
# systemctl is-enabled test-app.service
或者,您也可以同时启用和启动该服务,如图所示。
# systemctl enable --now test-app.service
要停止/停用该服务,请运行 systemctl stop 命令,如下所示:
# systemctl stop test-app.service
要重新启动服务,请运行 systemctl restart 命令,如下所示:
# systemctl restart test-app.service
您还可以使用 systemctl disable 命令禁用服务以防止它在系统启动时启动。您可以使用 systemctl is-enable 命令检查服务是否已启用,如下所示:
# systemctl disable test-app.service
# systemctl is-disabled test-app.service
或者,您可以同时禁用和停止它,如图所示。
# systemctl disable --now test-app.service
有关管理 systemd 服务和其他资源的更多详细信息,请运行:
# man systemctl
