如何在 Ubuntu 20.04 上使用 Grafana 和 Prometheus 监控 MongoDB
作者选择了 Write for DOnations 计划。
介绍
数据库管理员避免性能或内存问题至关重要。时间序列数据等工具。 Grafana 是一个用于交互式可视化和分析的开源 Web 应用程序。它允许您从大量数据源中提取数据、查询这些数据并将其显示在可自定义的图表上以便于分析。还可以设置警报,以便您可以快速轻松地收到意外行为的通知。将它们结合使用可以让您收集、监控、分析和可视化来自您的 MongoDB 实例的数据。
在本教程中,您将设置一个 MongoDB 数据库,并使用 Prometheus 作为数据源使用 Grafana 对其进行监控。为此,您需要将 MongoDB 导出器配置为 Prometheus 目标,以便 Prometheus 可以抓取您的数据库指标并将它们提供给 Grafana。
先决条件
要学习本教程,您需要:
- 一台 Ubuntu 20.04 服务器,非 root 用户拥有
sudo权限和配置了ufw的防火墙,您可以按照 Ubuntu 初始服务器设置指南进行操作20.04. - MongoDB 安装在 Ubuntu 20.04 服务器上,您可以按照教程如何在 Ubuntu 20.04 上安装 MongoDB 进行操作。
- Grafana 安装在 Ubuntu 20.04 服务器上,您可以按照教程“如何在 Ubuntu 20.04 上安装和保护 Grafana”中的第 1 步到第 4 步进行操作。
要安装 Grafana,您需要具备以下条件:
- 一个完全注册的域名。本教程始终使用
your_domain。您可以在 Freenom 上购买域名,或使用您选择的域名注册商。 - 为您的服务器设置的以下 DNS 记录。如果您使用的是 DigitalOcean,您可以按照如何添加域一文了解有关如何添加它们的详细信息。
- 一条 A 记录,其中
your_domain指向您服务器的公共 IP 地址。 - 带有
www.your_domain的 A 记录指向您服务器的公共 IP 地址。
第 1 步 — 安装和配置 Prometheus
Prometheus 是一个开源系统监控和警报工具包,用于收集指标并将其存储为时间序列数据。也就是说,度量信息与记录时的时间戳一起存储。在此步骤中,您将安装 Prometheus 并将其配置为作为服务运行。
安装普罗米修斯
首先,您需要安装 Prometheus。首先登录到您的服务器并更新包列表,如下所示:
- sudo apt update
接下来,您将为 Prometheus 创建配置和数据目录。要创建名为
prometheus的配置目录,请运行以下命令:- sudo mkdir -p /etc/prometheus
接下来,创建数据目录:
- sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/prometheus
创建目录后,您将下载压缩的安装文件。 Prometheus 安装文件以压缩文件中的预编译二进制文件形式提供。要下载 Prometheus,请访问下载页面。
要下载版本
2.31.0,请运行以下命令,根据需要替换版本号:- wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.31.0/prometheus-2.31.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
下载后,解压缩 tarball 文件:
- tar -xvf prometheus-2.31.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
提取文件后,导航到 Prometheus 文件夹:
- cd prometheus-2.31.0.linux-amd64
然后,将
prometheus和promtool二进制文件移动到/usr/local/bin/目录:- sudo mv prometheus promtool /usr/local/bin/
接下来,您会将与 Prometheus 相关的所有文件移动到一个位置:
/etc/prometheus/。要移动consoles目录中的控制台文件和console_libraries目录中的库文件,请运行以下命令:- sudo mv consoles/ console_libraries/ /etc/prometheus/
控制台和控制台库文件用于启动 Prometheus GUI。这些文件将与配置文件一起保存,以便在启动服务时可以使用它们。
最后将
prometheus.yml模板配置文件移动到/etc/prometheus/目录下:- sudo mv prometheus.yml /etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
prometheus.yml是模板配置文件,您将在其中配置 Prometheus 的端口以及启动服务时要使用的文件。要检查安装的 Prometheus 版本,请运行以下命令:
- prometheus --version
你会收到类似这样的输出:
Outputprometheus, version 2.31.0 (branch: HEAD, revision: b41e0750abf5cc18d8233161560731de05199330) build user: root@0aa1b7fc430d build date: 20220714-15:13:18 go version: go1.18.4 platform: linux/amd64在本节中,您安装了 Prometheus 并验证了其版本。接下来,您将把它作为一项服务启动。
将 Prometheus 作为服务运行
现在您已经安装了 Prometheus,您将配置它作为服务运行。
在创建系统文件来完成此操作之前,您需要创建一个 Prometheus 组和用户。您需要一个拥有必要目录所有者访问权限的专用用户。要创建
prometheus组,请运行以下命令:- sudo groupadd --system prometheus
接下来,创建一个
prometheus用户并将其分配给您刚刚创建的prometheus组:- sudo useradd -s /sbin/nologin --system -g prometheus prometheus
如下更改目录所有权和权限,以便专用用户具有正确的权限:
- sudo chown -R prometheus:prometheus /etc/prometheus/ /var/lib/prometheus/
- sudo chmod -R 775 /etc/prometheus/ /var/lib/prometheus/
接下来,您将创建服务文件以将 Prometheus 作为服务运行。使用
nano或您最喜欢的文本编辑器,创建一个名为prometheus.service的systemd服务文件:- sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service
添加以下代码行:
[Unit] Description=Prometheus Wants=network-online.target After=network-online.target [Service] User=prometheus Group=prometheus Restart=always Type=simple ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/prometheus \ --config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \ --storage.tsdb.path=/var/lib/prometheus/ \ --web.console.templates=/etc/prometheus/consoles \ --web.console.libraries=/etc/prometheus/console_libraries \ --web.listen-address=0.0.0.0:9090 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target使用此代码,您可以将 Prometheus 配置为使用
ExecStart块中列出的文件来运行服务。服务文件告诉systemd使用配置文件/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml作为prometheus用户运行 Prometheus 并存储其数据在/var/lib/prometheus目录中。您还可以将 Prometheus 配置为在端口9090上运行。 (systemd服务文件的详细信息超出了本教程的范围,但您可以在了解 Systemd 单元和单元文件中了解更多信息。)保存并关闭您的文件。如果使用
nano,请按CTRL+X,然后按Y。现在,启动 Prometheus 服务:
- sudo systemctl start prometheus
使 Prometheus 服务在启动时运行:
- sudo systemctl enable prometheus
您可以使用以下命令检查服务状态:
- sudo systemctl status prometheus
输出将确认该服务是
active (running):● prometheus.service - Prometheus Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/prometheus.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-08-05 18:06:05 UTC; 13s ago Main PID: 7177 (prometheus) Tasks: 6 (limit: 527) Memory: 21.0M CGroup: /system.slice/prometheus.service └─7177 /usr/local/bin/prometheus --config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml --storage.tsdb.path=/var/lib/prometheus/ --web.console.template>要访问 Prometheus,请启动浏览器并访问服务器的 IP 地址和端口
9090:http://your_server_ip:9090。注意:要访问 Prometheus Web 控制台,您可能需要在服务器上允许端口
9090。要检查您当前的 UFW 规则集,请运行以下命令:- sudo ufw status
如果尚未允许端口
9090,您可以使用以下命令添加它:- sudo ufw allow 9090
您现在可以访问 Prometheus Web 控制台:
在此步骤中,您安装了 Prometheus 并将其配置为作为服务运行。接下来,您将使用 MongoDB 导出器将您的 MongoDB 数据库绑定到 Prometheus。
第 2 步 — 配置 MongoDB 导出器
Prometheus 通过抓取目标来收集指标。在此步骤中,您将安装 MongoDB 导出器并将其配置为 Prometheus 目标,以便 Prometheus 可以从您的 MongoDB 实例收集数据。
安装 MongoDB 导出器
在本节中,您将安装 MongoDB 导出器。首先,为导出器创建一个目录并导航到它:
- mkdir mongodb-exporter
- cd mongodb-exporter
可以从 Github 下载 MongoDB 导出器。导出器作为存档中的二进制文件出现,但您会将其配置为服务。使用以下命令下载二进制文件:
- wget https://github.com/percona/mongodb_exporter/releases/download/v0.7.1/mongodb_exporter-0.7.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
接下来,将下载的存档解压缩到当前文件夹中:
- tar xvzf mongodb_exporter-0.7.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
最后,将
mongodb_exporter二进制文件移动到usr/local/bin/:- sudo mv mongodb_exporter /usr/local/bin/
在本节中,您安装了 MongoDB 导出器。接下来,您将启用 MongoDB 身份验证并创建一个用于监控的用户。
启用 MongoDB 身份验证
在本节中,您将为 MongoDB 导出器设置 MongoDB 身份验证并创建一个用户来监控集群的指标。
首先使用
mongo连接到您的 MongoDB 实例:- mongo
您将为您的导出器创建一个具有集群监视器角色的管理员帐户。切换到
admin数据库:- use admin
切换到
admin数据库后,创建一个具有clusterMonitor角色的用户:- db.createUser({user: "test",pwd: "testing",roles: [{ role: "clusterMonitor", db: "admin" },{ role: "read", db: "local" }]})
您将收到以下输出:
Successfully added user: { "user" : "test", "roles" : [ { "role" : "clusterMonitor", "db" : "admin" }, { "role" : "read", "db" : "local" } ] }创建用户后,退出 MongoDB shell:
- exit
接下来,使用适当的身份验证凭据设置您的 MongoDB URI 环境变量:
export MONGODB_URI=mongodb://test:testing@localhost:27017您设置
MONGODB_URI以指定使用您之前设置的身份验证凭据的mongodb实例(test用户和testing密码)。27017是mongodb实例的默认端口。设置环境变量时,它优先于存储在配置文件中的配置文件。要检查 MongoDO URI 环境变量是否设置正确,请运行以下命令:
- env | grep mongodb
您将收到以下输出:
MONGODB_URI=mongodb://mongodb_exporter:password@localhost:27017在本节中,您创建了一个具有
clusterMonitor角色的 MongoDB 用户,这有助于监控集群指标。接下来,您将配置 MongoDB 导出器以作为服务运行。为 MongoDB 导出器创建服务
在本节中,您将为 MongoDB 导出器创建一个系统文件并将其作为服务运行。
导航到
/lib/systemd/system并使用nano或您最喜欢的文本编辑器为导出器创建一个新的服务文件:- cd /lib/systemd/system/
- sudo nano mongodb_exporter.service
将以下配置粘贴到您的服务文件中:
[Unit] Description=MongoDB Exporter User=prometheus [Service] Type=simple Restart=always ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/mongodb_exporter [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target此服务文件告诉
systemd在prometheus用户下将 MongoDB exporter 作为服务运行。ExecStart将从usr/local/bin/运行mongodb_exporter二进制文件。有关systemd服务文件的更多信息,请查看了解 Systemd 单元和单元文件。保存并关闭您的文件。
接下来,重新启动系统守护进程以重新加载单元文件:
- sudo systemctl daemon-reload
现在,开始你的服务:
- sudo systemctl start mongodb_exporter.service
要检查 MongoDB 导出器服务的状态,请运行以下命令:
- sudo systemctl status mongodb_exporter.service
输出将确认该服务是
active (running):● mongodb_exporter.service - MongoDB Exporter Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mongodb_exporter.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2022-08-05 18:18:38 UTC; 1 weeks 3 days ago Main PID: 7352 (mongodb_exporte) Tasks: 5 (limit: 527) Memory: 14.2M CGroup: /system.slice/mongodb_exporter.service └─7352 /usr/local/bin/mongodb_exporter为确保一切都按预期工作,请导航到项目根目录并在导出器运行的端口
9216上运行 curl 命令:- cd ~
- sudo curl http://localhost:9216/metrics
输出会很长,并且包含类似这样的行:
Output# HELP go_gc_duration_seconds A summary of the GC invocation durations. # TYPE go_gc_duration_seconds summary go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.25"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.5"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="0.75"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds{quantile="1"} 0 go_gc_duration_seconds_sum 0 go_gc_duration_seconds_count 0 # HELP go_goroutines Number of goroutines that currently exist. # TYPE go_goroutines gauge go_goroutines 11 # HELP go_memstats_alloc_bytes Number of bytes allocated and still in use. # TYPE go_memstats_alloc_bytes gauge go_memstats_alloc_bytes 1.253696e+06 # HELP go_memstats_alloc_bytes_total Total number of bytes allocated, even if freed. # TYPE go_memstats_alloc_bytes_total counter go_memstats_alloc_bytes_total 1.253696e+06 # HELP go_memstats_buck_hash_sys_bytes Number of bytes used by the profiling bucket hash table. # TYPE go_memstats_buck_hash_sys_bytes gauge go_memstats_buck_hash_sys_bytes 3054 # HELP go_memstats_frees_total Total number of frees. # TYPE go_memstats_frees_total counter go_memstats_frees_total 2866 # HELP go_memstats_gc_sys_byte . . . # HELP mongodb_asserts_total The asserts document reports the number of asserts on the database. While assert errors are typically uncommon, if there are non-zero values for the asserts, you should check the log file for the mongod process for more information. In many cases these errors are trivial, but are worth investigating. # TYPE mongodb_asserts_total counter mongodb_asserts_total{type="msg"} 0 mongodb_asserts_total{type="regular"} 0 mongodb_asserts_total{type="rollovers"} 0 mongodb_asserts_total{type="user"} 19 mongodb_asserts_total{type="warning"} 0 # HELP mongodb_connections The connections sub document data regarding the current status of incoming connections and availability of the database server. Use these values to assess the current load and capacity requirements of the server # TYPE mongodb_connections gauge mongodb_connections{state="available"} 51198 mongodb_connections{state="current"} 2 # HELP mongodb_connections_metrics_created_total totalCreated provides a count of all incoming connections created to the server. This number includes connections that have since closed # TYPE mongodb_connections_metrics_created_total counter mongodb_connections_metrics_created_total 6 # HELP mongodb_exporter_build_info A metric with a constant '1' value labeled by version, revision, branch, and goversion from which mongodb_exporter was built. # TYPE mongodb_exporter_build_info gauge mongodb_exporter_build_info{branch="v0.7.1",goversion="go1.11.10",revision="3002738d50f689c8204f70f6cceb8150b98fa869",version="0.7.1"} 1 # HELP mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds Duration of the last scrape of metrics from MongoDB. # TYPE mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds gauge mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_duration_seconds 0.003641888 # HELP mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_error Whether the last scrape of metrics from MongoDB resulted in an error (1 for error, 0 for success). # TYPE mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_error gauge mongodb_exporter_last_scrape_error 0 . . . ...输出确认 MongoDB 导出器正在收集指标,例如
mongodb版本、metrics-document和连接详细信息。在本节中,您将 MongoDB 导出器设置为服务并从 MongoDB 收集指标。接下来,您将导出器配置为 Prometheus 的目标。
将 MongoDB Exporter 配置为 Prometheus 目标
在本节中,您会将 MongoDB 导出器配置为 Prometheus 目标。导航到包含 Prometheus 配置文件的目录:
- cd /etc/prometheus/
使用
nano或您最喜欢的文本编辑器,打开文件进行编辑:- sudo nano prometheus.yml
通过将突出显示的行复制到您的文件中,将 MongoDB 导出器添加为目标:
# A scrape configuration containing exactly one endpoint to scrape: # Here it's Prometheus itself. scrape_configs: # The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config. - job_name: "prometheus" static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090", "localhost:9216"]9216是 MongoDB 导出器的默认端口。保存并关闭您的文件。
添加目标后,重启 Prometheus:
- sudo systemctl restart prometheus
导航到
http://localhost:9090/targets以验证 Prometheus 正在抓取您新添加的导出器。注意:如果您使用的是远程服务器,则可以通过导航到
http://your_server_ip:9090/targets查看目标。您还可以使用端口转发在本地查看目标。为此,请在本地计算机上打开一个新终端并输入以下命令:- ssh -L 9090:localhost:9090 your_non_root_user@your_server_ip
连接到服务器后,在本地计算机的 Web 浏览器上导航到
http://localhost:9090/targets。您将访问 Prometheus 目标列表:
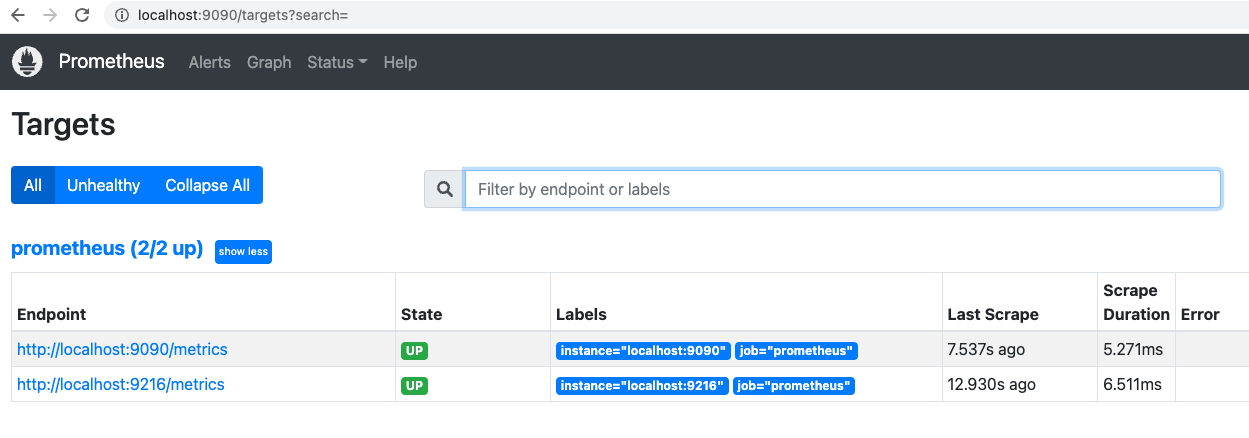
9090端点是 Prometheus 自己抓取的。9216端点是 MongoDB 导出器,它确认您的配置按预期工作。在此步骤中,您安装了 MongoDB 导出器并将其配置为 Prometheus 目标以收集指标。接下来,您将在 Grafana Web 控制台中创建一个 MongoDB 仪表板,以查看和分析这些指标。
第 3 步 — 在 Grafana 中构建 MongoDB 仪表板
在此步骤中,您将构建一个仪表板以在 Grafana 中可视化您的 MongoDB 数据。为此,您将在 Grafana 中添加 Prometheus 作为数据源,并将 MongoDB 仪表板从 MongoDB 概览仪表板导入到您的 Grafana 实例中。首先,您将 Prometheus 设置为 Grafana 数据源。
作为先决条件的一部分,您安装并保护了 Grafana。导航到位于
your_domain:3000的 Grafana 实例,并使用您在先决条件期间创建的凭据登录。在左侧面板中,单击配置的齿轮图标,然后选择数据源:
点击添加数据源:

然后选择普罗米修斯:
在下一个屏幕上,您将为 Prometheus 数据源配置设置:
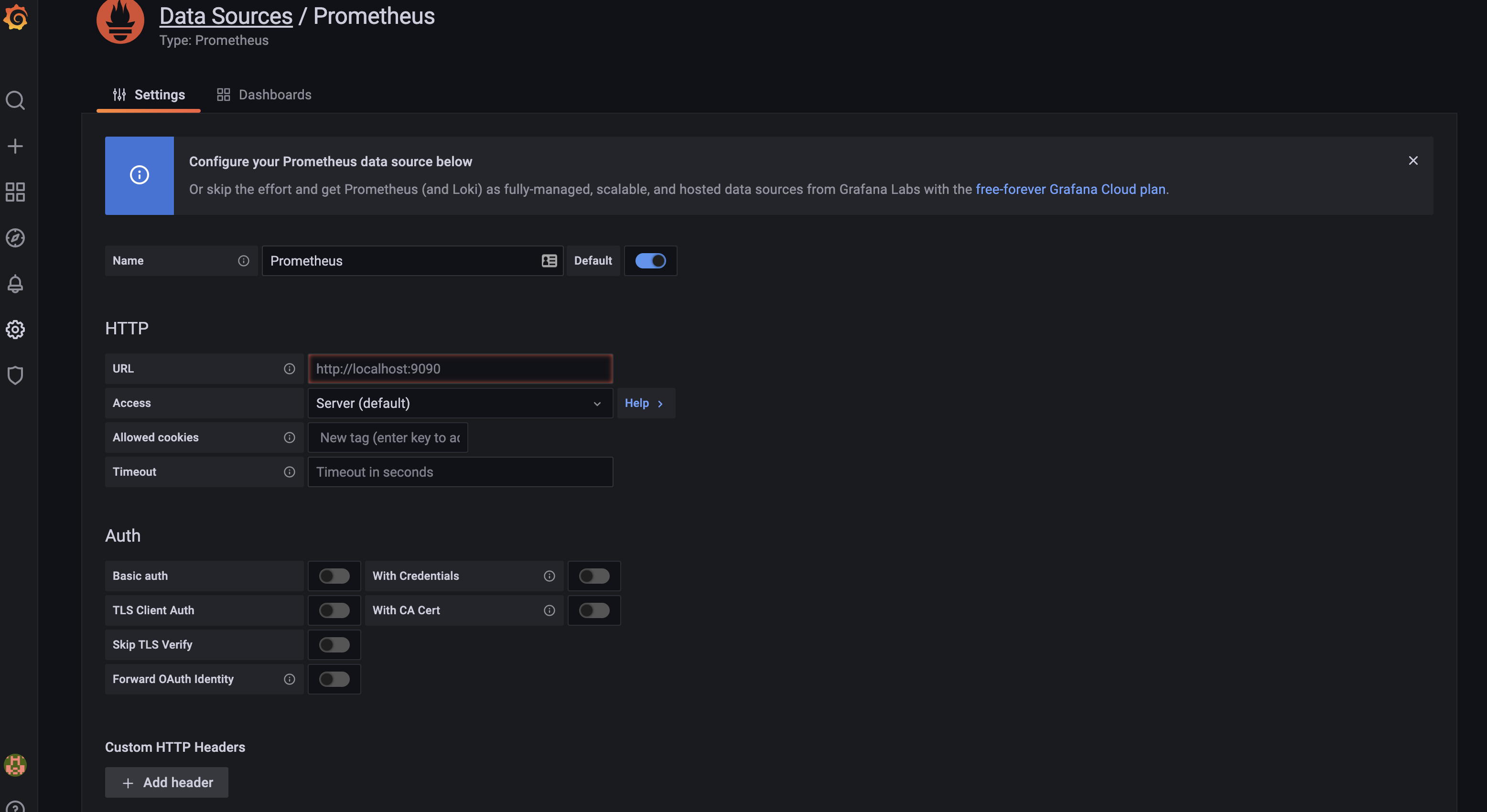
在 URL 字段中,提供您的 Prometheus 实例的 URL:
http://your_server_ip:9090/单击屏幕底部的保存和测试。现在添加 Prometheus 作为 Grafana 的数据源。
接下来,您将为 Grafana 导入 MongoDB 概述仪表板。您可以通过上传 JSON 文件或导入仪表板 ID 来导入仪表板,您可以在仪表板的 Grafana 产品文档中找到这些 ID。在这里,您将使用仪表板 ID 导入仪表板。
在左侧菜单中,单击“创建”的加号图标并选择“导入”。从那里,您应该被带到导入页面:
在这里,您可以上传仪表板的 JSON 文件或粘贴 Grafana 仪表板 ID:

添加 Grafana 仪表板 ID,您可以在 MongoDB 概览仪表板的 Grafana 页面上找到它:
https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/7353许多仪表板可用。您可以通过访问仪表板上的 Grafana 页面找到更多信息。
添加仪表板 ID 后,单击加载。
现在将打开一个选项页面,您可以在其中为仪表板提供名称,选择仪表板的文件夹,然后选择数据源。您可以将仪表板和文件夹名称保留为默认值。对于数据源,选择 Prometheus。填写选项后,单击“导入”。
将创建仪表板:

您的仪表板将显示您的 MongoDB 数据库的实时更新,包括命令操作、连接、游标、文档操作和排队操作。 (有关更多详细信息,请查看 MongoDB 概览仪表板的 Percona 文档。)
结论
在本文中,您设置了一个 Grafana 仪表板来监控您的 MongoDB 数据库的 Prometheus 指标,这使您能够通过 GUI 仪表板监控您的数据库。首先,您安装了 Prometheus 并配置了 MongoDB 导出器。然后,您将 Prometheus 添加为 Grafana 中的数据源,您可以在其中监控和可视化来自 MongoDB 实例的数据。
现在您已经为 MongoDB 建立了一个完全可操作的监控管道,您可以进行更深入的挖掘。首先,尝试探索 Grafana 中的其他仪表板。
要了解有关 MongoDB 的更多信息,请查看我们的如何使用 MongoDB 管理数据教程系列。
要快速访问完全可用的数据库环境,请查看 DigitalOcean 的 MongoDB 托管数据库。
- 一条 A 记录,其中
