在 Linux 命令行中列出磁盘的 6 种不同方法
这个详细的指南将为您提供足够的信息来开始使用 Emacs,并提供足够的额外信息让您想要更多。
有多种方法可以通过 Linux 命令行列出系统中存在的所有硬盘驱动器。
请记住,硬盘驱动器可以物理连接、虚拟连接甚至模拟(例如:当您使用 EMC、Sun 或 IBM 等存储设备时)。
这里有一些可以列出硬盘驱动器的不同命令,请记住还有其他命令,但这些可能是最常用且易于完成工作的命令。
列出 Linux 中的硬盘
请注意,其中一些命令实际上是磁盘分区工具,列出磁盘分区是它们的功能之一。
让我们看看在 Linux 中可以使用哪些命令来显示磁盘信息。
1. df
Linux 中的 df 命令可能是最常用的命令之一。它列出了实际的“磁盘空间使用情况”,并且可以为您提供有关整个系统中正在使用哪些硬盘(或当前磁盘空间)的信息。
最常见的使用方法是使用 -h 参数,这意味着“人类可读”(因为我们不是机器,对吧?):
user@system:~$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
udev 7.8G 0 7.8G 0% /dev
tmpfs 1.6G 3.5M 1.6G 1% /run
/dev/sda2 468G 204G 242G 46% /
tmpfs 7.8G 109M 7.7G 2% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 4.0K 5.0M 1% /run/lock
tmpfs 7.8G 0 7.8G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/loop0 7.5M 7.5M 0 100% /snap/canonical-livepatch/54
/dev/loop1 90M 90M 0 100% /snap/core/6034
/dev/loop2 5.0M 5.0M 0 100% /snap/canonical-livepatch/50
/dev/loop4 90M 90M 0 100% /snap/core/6130
/dev/loop3 4.8M 4.8M 0 100% /snap/canonical-livepatch/49
/dev/loop5 89M 89M 0 100% /snap/core/5897
/dev/sda1 511M 6.1M 505M 2% /boot/efi
tmpfs 1.6G 16K 1.6G 1% /run/user/121
tmpfs 1.6G 44K 1.6G 1% /run/user/1000正如您所看到的,第一列是当前逻辑名称(或者您可以在系统中找到它的名称),第二列是它们每个有多大,第三列是当前使用了多少(以字节为单位) ,第四列是每个当前可用的数量(以字节为单位),第五列是已使用的数量(以%为单位),第六列也是最后一列是它在 Linux 系统中物理安装的位置。
2、fdisk
fdisk 是管理员中的另一个常见选项。它当前列出了系统中的不同分区(与硬盘驱动器有关,因为硬盘驱动器可以分为多个分区)。
user@system:~$ fdisk -l
Disk /dev/loop0: 7.5 MiB, 7811072 bytes, 15256 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 89.5 MiB, 93818880 bytes, 183240 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop2: 4.9 MiB, 5148672 bytes, 10056 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop3: 4.7 MiB, 4919296 bytes, 9608 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop4: 89.5 MiB, 93835264 bytes, 183272 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop5: 88.2 MiB, 92483584 bytes, 180632 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/sda: 477 GiB, 512110190592 bytes, 1000215216 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: 129F4EE6-2A54-4639-BFCA-2CC09DFC8566
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1050623 1048576 512M EFI System
/dev/sda2 1050624 1000214527 999163904 476.4G Linux filesystem 这将返回每个分区的全部空间量(以 GB 或 MB 为单位)、全部字节数和全部扇区量,作为摘要,它还为您提供开始和结束扇区、磁盘空间量(以字节为单位)和分区类型。
提示:SATA磁盘通常带有sd标签。
3. lsblk
这个稍微复杂一些,但是可以完成工作,因为它列出了所有块设备。它将为您提供所有设备的非常简单的列表:
user@system:~$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
loop0 7:0 0 7.5M 1 loop /snap/canonical-livepatch/54
loop1 7:1 0 89.5M 1 loop /snap/core/6034
loop2 7:2 0 4.9M 1 loop /snap/canonical-livepatch/50
loop3 7:3 0 4.7M 1 loop /snap/canonical-livepatch/49
loop4 7:4 0 89.5M 1 loop /snap/core/6130
loop5 7:5 0 88.2M 1 loop /snap/core/5897
sda 8:0 0 477G 0 disk
├─sda1 8:1 0 512M 0 part /boot/efi
└─sda2 8:2 0 476.4G 0 part /它可能比其他磁盘更直观,因为它甚至以可视方式显示每个磁盘的分区(如上例中的 sda)。它还提供有关每个分区和磁盘的总大小以及每个分区和磁盘的物理位置的信息。当您需要安装要使用的东西(例如 USB 记忆棒或类似设备)时,这非常常用,这样您就可以知道它在哪里,以便继续安装它。
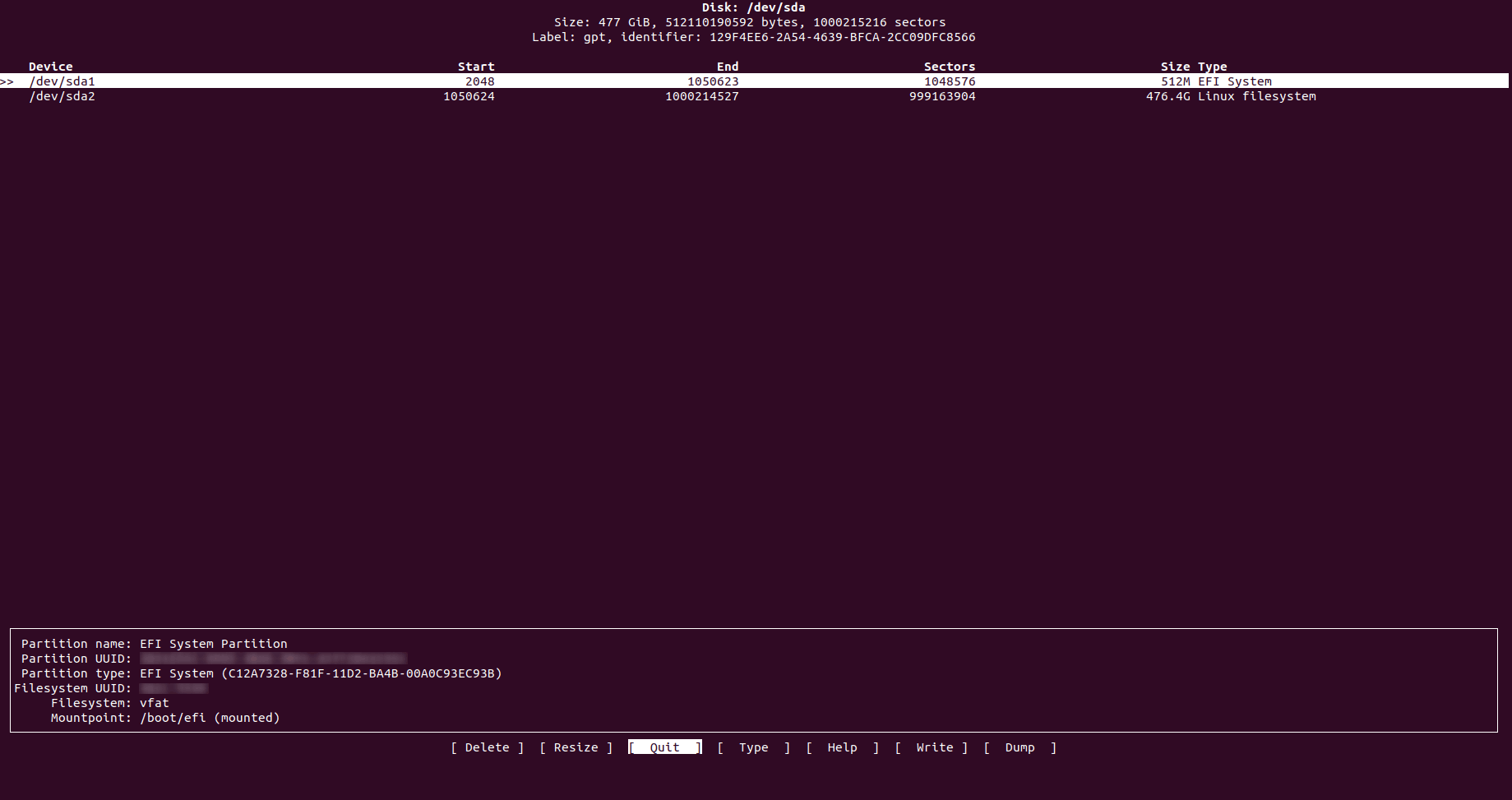
4.cfdisk
cfdisk 可能是 GUI(图形用户界面)中最先进的一种,因为它绝对是可视化和交互式的。它首先允许列出系统中的所有磁盘/分区,但它也允许您通过选择它们然后应用“删除”、“调整大小”、“类型”(更改分区类型)和“写入”等操作来管理它们” 对分区进行的更改。
它还为您提供有关每个分区和磁盘的非常友好的信息,因为它为您提供每个分区柱面的开始和结束位置、每个分区使用的扇区数量以及每个分区的完整大小及其类型。例如,它不会告诉您已使用或免费使用的数量。
5.分手了
这与前面提到的类似,它列出了所有分区并允许管理它们。它的主要区别在于,它还会告诉您硬盘的品牌和型号,甚至其中使用的连接类型(scsi、sata 等)和磁盘总大小。
user@system:~$ sudo parted -l
Model: ATA LITEON CV1-8B512 (scsi)
Disk /dev/sda: 512GB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
1 1049kB 538MB 537MB fat32 EFI System Partition boot, esp6. sfdisk
这与 fdisk 非常相似,但是 sfdisk 允许您查看物理卷和逻辑卷,并且还为您提供实际物理卷分区的“摘要”,包括柱面(开始和结束)、扇区、尺寸和类型。
可能“s”代表“super”,因为它是具有超能力的 fdisk:
user@system:~$ sudo sfdisk -l
Disk /dev/loop0: 88.2 MiB, 92483584 bytes, 180632 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop1: 4.7 MiB, 4919296 bytes, 9608 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop2: 4.9 MiB, 5148672 bytes, 10056 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop3: 89.5 MiB, 93818880 bytes, 183240 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop4: 7.5 MiB, 7811072 bytes, 15256 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/loop5: 89.5 MiB, 93835264 bytes, 183272 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/sda: 477 GiB, 512110190592 bytes, 1000215216 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: 129F4EE6-2A54-4639-BFCA-2CC09DFC8566
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/sda1 2048 1050623 1048576 512M EFI System
/dev/sda2 1050624 1000214527 999163904 476.4G Linux filesystem这些命令至少应该允许您查看系统中拥有哪些逻辑卷、分区和硬盘驱动器,并根据您需要的任何原因使用这些信息,只是为了了解更多信息或操作其中任何一个。
这些命令中的大多数还为您提供了随意修改和操作分区的管理功能,因此请务必负责任地使用它们。
如果您喜欢检查系统信息,请阅读有关在 Linux 命令行中获取处理器信息的文章。
如果您有任何问题或建议,请在评论部分告诉我。