C 和 Linux 的定时器机制
使用 Linux 和 C 获得对计时函数的细粒度控制。
计时器机制允许您安排操作系统内核在预定时间过去时通知应用程序。您通常会通过提供两条信息来使用它们。首先,您需要指定计时器在发出通知之前应花费多长时间。其次,您需要准备一个回调函数,以便在通知发生时执行操作。
传统的定时器方法
Linux 和基于 Unix 的系统中的计时器机制已经发展到满足各种需求。不同的方法可以帮助您解决不同类型的问题。但是,您经常会看到 alarm() 机制的第一个版本仍在使用。
闹钟功能是定时器最简单的使用方式;这是它的原型:
unsigned int alarm(unsigned int seconds);
使用此方法,您只能指定以整秒为单位的时间。当时间到时,操作系统会向您的应用程序发送 SIGALRM 信号。要在应用程序中处理计时器的到期,您还应该定义一个回调函数。
这是信号处理函数的示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
void timer_callback(int signum)
{
time_t now = time(NULL);
printf("Signal %d caught on %li", signum, now);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGALRM, timer_callback);
alarm(1);
sleep(3);
return 0;
}
此代码在 1 秒后引发 SIGALRM 信号。如果您想将计时器延迟增加到五秒,只需调用 alarm(5) 即可。要停止计时器,请传递值 0:alarm(0)。
当时间到时,您使用的计时器不会定期重新启动。例如,如果您想再延迟一秒钟,则应该通过再次调用 alarm() 来重新启动该机制。
尽管该方法易于使用,但也有一些缺点:
- 一次只有一个计时器。
- 没有周期性计时器支持。
- 您只能以整秒的倍数给出时间段。
- 无法知道计时器还剩多少时间。
将上面给出的示例代码保存为alarm.c。当你编译并运行它时,程序将在一秒后调用timer_callback函数。然后,由于 sleep(3) 线路,它将等待剩余的两秒,然后终止。
$ gcc -o alarm alarm.c
$ time ./alarm
Signal 14 caught on 1653490465
real 0m1.004s
user 0m0.000s
sys 0m0.003s
使用time命令的原因是为了能够看到时间。但如果你看一下结果,总的运行时间还不到三秒。这是由于第一秒时从 alarm(1) 发出的 SIGALRM 信号,而 sleep(3) 引起的 syscall功能正在运行。当此信号到达时,它会中断为 sleep(3) 启动的系统调用。
使用间隔定时器
间隔计时器机制首先在 4.2 BSD 版本中可用。后来它被 POSIX 标准化。与传统的基于alarm()的定时器方法相比,它的主要优点是:
- 提供微秒级分辨率。
- 它允许通过三种不同的模式更详细地控制时间测量。
- 可以设置一次并使其定期工作。
- 可以找出它在任何给定时刻存在的时间。
用于间隔定时器操作的函数原型如下:
#include <sys/time.h>
int setitimer(int which, const struct itimerval *newValue, struct itimerval *oldValue);
int getitimer(int which, struct itimerval *value);
struct itimerval
{
struct timeval itInterval; // next value
struct timeval itValue; // current value
};
struct timeval
{
long tv_sec;
long tv_usec;
};
如果要设置间隔计时器,则需要使用 itimerval 结构。您需要使用此结构体作为第二个参数传递一个值给 settimer 函数。
例如,间隔计时器将通知您的应用程序 1 秒,然后每 300 毫秒通知一次,可以设置如下:
struct itimerval newTimer;
struct itimerval oldTimer;
newTimer.itValue.tv_sec = 1;
newTimer.itValue.tv_usec = 0;
newTimer.itInterval.tv_sec = 0;
newTimer.itInterval.tv_usec = 300 * 1000;
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &newTimer, &oldTimer);
如果在设置新值之前有一个间隔计时器处于活动状态,则其值将传输到为函数的第三个参数指定的 itimerval 类型的变量地址。
您可以使用间隔计时器机制设置三种不同类型的计时器。在setitimer()的第一个参数中指定定时器类型:
Timer Type | Signal | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
ITIMER_REAL | SIGALRM | Independent of the time spent by the application, calculated over the total elapsed time. |
ITIMER_VIRTUAL | SIGVTALRM | Calculated over the time the application is running in user mode only. |
ITIMER_PROF | SIGPROF | Calculated over the sum of the time spent by the application in both user and system modes. |
从该表中可以看出,ITIMER_REAL类型发送SIGALRM信号,就像alarm()函数一样。
在同一个应用程序中使用间隔计时器和 alarm() 会造成混乱。虽然您可以使用 gettimer() 再次检查剩余时间,但同时使用它们是没有意义的。
下面是使用调试头定义信号处理函数的示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "./debug.h"
void timer_callback(int signum)
{
struct timeval now;
gettimeofday(&now, NULL);
printf("Signal %d caught on %li.%03li ", signum, now.tv_sec, now.tv_usec / 1000);
}
int main()
{
unsigned int remaining = 3;
struct itimerval new_timer;
struct itimerval old_timer;
new_timer.it_value.tv_sec = 1;
new_timer.it_value.tv_usec = 0;
new_timer.it_interval.tv_sec = 0;
new_timer.it_interval.tv_usec = 300 * 1000;
setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &new_timer, &old_timer);
signal(SIGALRM, timer_callback);
while (sleep(remaining) != 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
debugf("sleep interrupted by signal");
else
errorf("sleep error %s", strerror(errno));
}
return 0;
}
上面的代码使用sleep()函数等待三秒。在此期间,间隔计时器运行,首先运行一秒,然后以 300 毫秒的间隔运行。
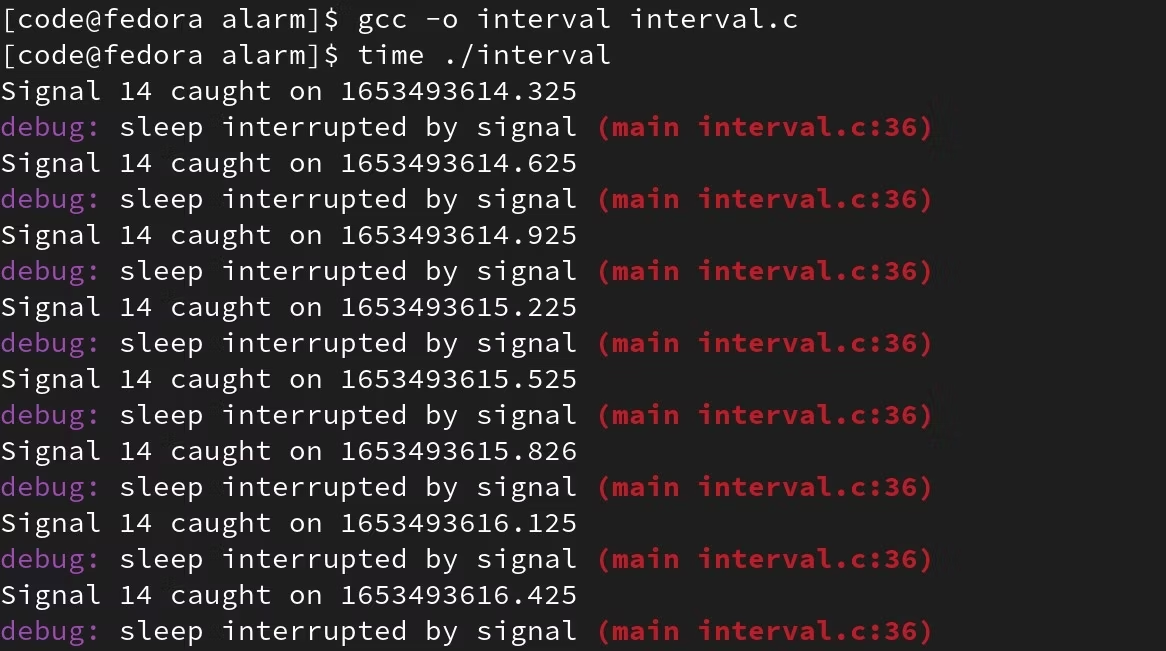
为了更好地理解,请保存并编译名为 interval.c 的示例代码:
$ gcc -o interval interval.c
$ time ./interval
Signal 14 caught on 1653493614.325
debug: sleep interrupted by signal (main interval.c:36)
Signal 14 caught on 1653493614.625
debug: sleep interrupted by signal (main interval.c:36)
Signal 14 caught on 1653493614.925
debug: sleep interrupted by signal (main interval.c:36)
Signal 14 caught on 1653493615.225
debug: sleep interrupted by signal (main interval.c:36)
Signal 14 caught on 1653493615.525
...
从定时器运行后的输出可以看出,它每 300 毫秒调用一次回调函数。
然而,等待一段时间后,您会发现应用程序并没有终止。它继续每 300 毫秒运行一次回调函数。如果增加间隔值(以毫秒为单位),您将看到应用程序终止。这是因为 sleep() 函数的使用区域。
在 Linux 中使用定时器的重要性
特别是对于实时应用来说,定时器机制非常重要。这也是一种用于性能优化的方案。您甚至可以使用它来测量应用程序中的正常运行时间或延迟。使用计时器机制来跟踪经过的时间和时间转换事件非常重要。